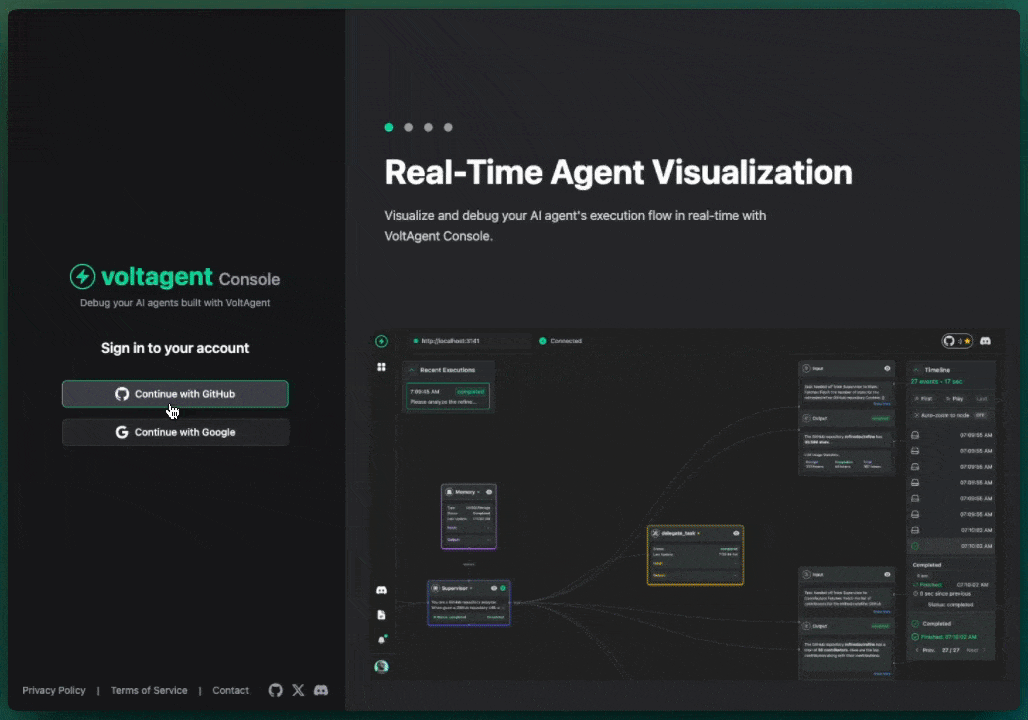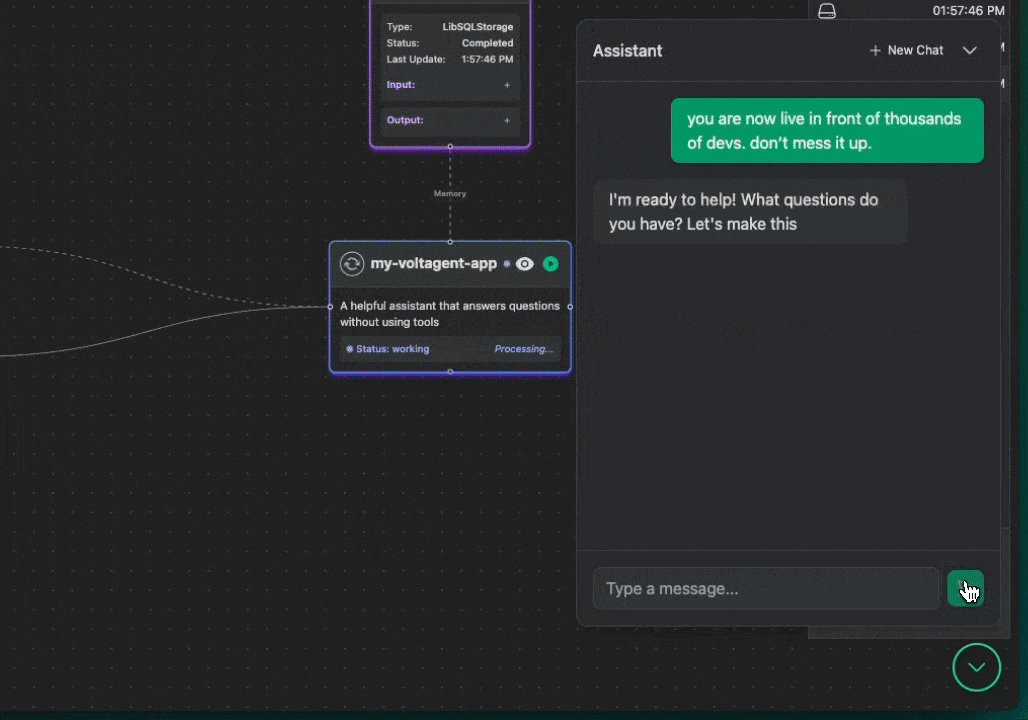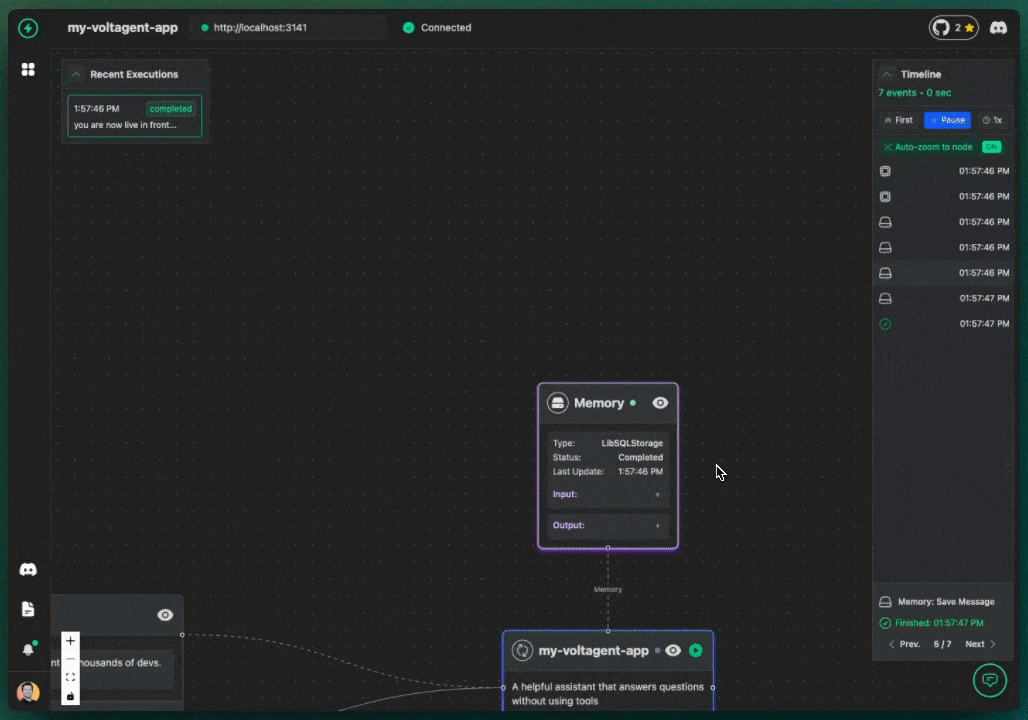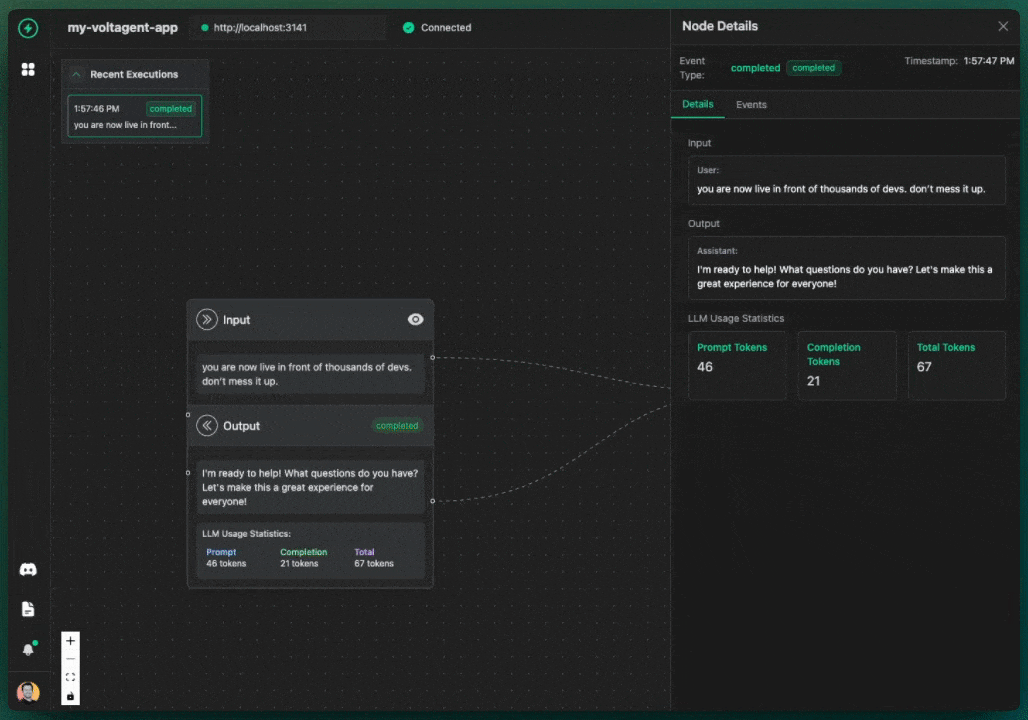
Overview
VoltAgent is an open source TypeScript framework for building and orchestrating AI agents. You can build production-ready agents with memory, workflows, tools, and built-in LLM observability.
Why VoltAgent?
- Production-Ready from Day One: Ship agents with built-in memory, workflows, and observability instead of building infrastructure from scratch.
- Code with Confidence: Full TypeScript support with type-safe tools, automatic inference, and compile time safety across your entire agent system.
- Debug Like a Pro: Built-in VoltOps observability lets you trace every decision, monitor performance, and optimize workflows in real-time without external tools.
- Build Complex Systems Simply: Orchestrate multi-agent teams with supervisor coordination, declarative workflows, and modular architecture that scales from prototypes to production.
Agent Development Platform
VoltAgent provides a complete platform for developing and monitoring AI agents through two complementary tools.
Core Framework
With the core framework, you can build intelligent agents with memory, tools, and multi-step workflows while connecting to any AI provider. Create sophisticated multi-agent systems where specialized agents work together under supervisor coordination.
📄️ Core Runtime
Define agents with typed roles, tools, memory, and model providers in one place so everything stays organized.
📄️ Workflow Engine
Describe multi-step automations declaratively rather than stitching together custom control flow.
📄️ Supervisors & Sub-Agents
Run teams of specialized agents under a supervisor runtime that routes tasks and keeps them in sync.
📄️ Tool Registry & MCP
Ship Zod-typed tools with lifecycle hooks and cancellation, and connect to Model Context Protocol servers without extra glue code.
📄️ LLM Compatibility
Swap between OpenAI, Anthropic, Google, or other providers by changing config, not rewriting agent logic.
📄️ Memory
Attach durable memory adapters so agents remember important context across runs.
📄️ Retrieval & RAG
Plug in retriever agents to pull facts from your data sources and ground responses (RAG) before the model answers.
📄️ Evals
Ship guardrails faster by running agent eval suites alongside your workflows.
📄️ Guardrails
Add safety checks and validation layers to ensure your agents behave correctly and safely.
Core Framework Example
import { VoltAgent, Agent } from "@voltagent/core";
import { honoServer } from "@voltagent/server-hono";
import { openai } from "@ai-sdk/openai";
const agent = new Agent({
name: "my-voltagent-app",
instructions: "A helpful assistant that answers questions without using tools",
// VoltAgent uses the AI SDK directly - pick any ai-sdk model
model: openai("gpt-4o-mini"),
});
// Serve your agent over HTTP (default port 3141)
new VoltAgent({
agents: { agent },
server: honoServer(),
});
Workflow Engine Example
import { createWorkflowChain, andThen, andAgent, Agent } from "@voltagent/core";
import { openai } from "@ai-sdk/openai";
import { z } from "zod";
// First, define an agent to be used in the workflow
const agent = new Agent({
name: "summarizer-agent",
instructions: "You are an expert at summarizing text.",
model: openai("gpt-4o-mini"),
});
// Then, create the workflow that uses the agent
const analysisWorkflow = createWorkflowChain({
id: "text-analysis-workflow",
name: "Text Analysis Workflow",
input: z.object({ text: z.string() }),
result: z.object({
summary: z.string(),
summaryWordCount: z.number(),
}),
})
// Step 1: Prepare the data
.andThen({
name: "trim-text",
execute: async (data) => ({
trimmedText: data.text.trim(),
}),
})
// Step 2: Call the AI agent for analysis
.andAgent(
(data) => `Summarize this text in one sentence: "${data.trimmedText}"`,
agent, // Uses the agent defined above
{
schema: z.object({ summary: z.string() }),
}
)
// Step 3: Process the AI's output
.andThen({
name: "count-summary-words",
execute: async (data) => ({
summary: data.summary,
summaryWordCount: data.summary.split(" ").length,
}),
});
Actions & Integrations
Connect agent or workflow outputs to external systems without writing custom plumbing. VoltOps ships with an Actions catalog (first release: Airtable) that you can explore from the console, test in place, and then call directly from code.
- Use the Actions drawer in VoltOps Console to pick an integration, select a credential, and provide sample payload values.
- Run the real provider test from the drawer, inspect the response, and copy the generated SDK snippet.
- Paste the snippet into your agent or workflow and replace the sample values with runtime data.
import { createVoltOpsClient } from "@voltagent/core";
const voltops = createVoltOpsClient({
publicKey: process.env.VOLT_PUBLIC_KEY!,
secretKey: process.env.VOLT_SECRET_KEY!,
});
await voltops.actions.airtable.createRecord({
credentialId: "cred_abc123",
baseId: "appXXXXXXXXXXXXXX",
tableId: "tblYYYYYYYYYYYY",
fields: {
Name: "Ada Lovelace",
Email: "ada@example.com",
},
typecast: true,
});
Bindings run inside VoltOps with observability, retries, and can be attached to agents or workflows using JSON transform templates. Additional providers will land in the same experience.
VoltOps LLM Observability Platform
VoltAgent comes with built-in VoltOps LLM observability to monitor and debug your agents in real-time with detailed execution traces, performance metrics, and visual dashboards. Inspect every decision your agents make, track tool usage, and optimize your workflows with built-in OpenTelemetry-based observability.